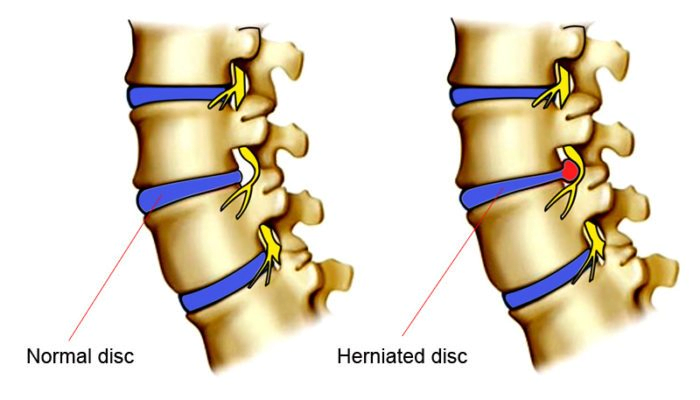
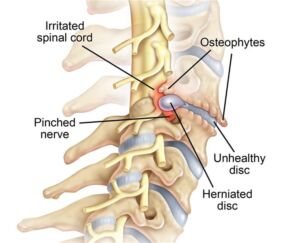
“A herniated disc (also called bulged, slipped or ruptured) is a fragment of the disc nucleus that is pushed out of the annulus, into the spinal canal through a tear or rupture in the annulus. Discs that become herniated usually are in an early stage of degeneration” (American Association of Neurological Surgeons, n.d.).
What causes a herniated disc?
There are multiple factors that can cause a disc herniation. One could simply slip and fall and cause the herniation, as well as any other strain or injury. On the other hand, age can play a huge role in the likeliness of obtaining a herniated disc. “Disc material degenerates naturally as one ages, and the ligaments that hold it in place begin to weaken. As this degeneration progresses, a relatively minor strain or twisting movement can cause a disc to rupture” (American Association of Neurological Surgeons, n.d.).
What are the symptoms of a herniated disc?
Typically, the patient would feel pain in the affected area. “If the herniated disc is not pressing on a nerve, the patient may experience a low backache or no pain at all. If it is pressing on a nerve, there may be pain, numbness or weakness in the area of the body to which the nerve travels” (American Association of Neurological Surgeons, n.d.).
How does one treat a disc herniation?
First and foremost, the doctor will create a treatment plan that is tailored to the patient’s needs. The treatment plan will differ per patient, due to the nature of its complexity. These treatment plans can include, but are not limited to, chiropractic adjustments, traction table/decompression, physical therapy, etc. “The doctor may recommend physical therapy. The therapist will perform an in-depth evaluation, which, combined with the doctor’s diagnosis, dictates a treatment specifically designed for patients with herniated discs. Therapy may include pelvic traction, gentle massage, ice and heat therapy, ultrasound, electrical muscle stimulation and stretching exercises. Pain medication and muscle relaxants may also be beneficial in conjunction with physical therapy” (American Association of Neurological Surgeons, n.d.). If condition worsens over time whilst performing all aspects of the treatment plan, the patient may discuss other options, such as surgery, with the doctor.
Work Cited
Herniated Disc. (n.d.). Retrieved July 07, 2020, from https://www.aans.org/Patients/Neurosurgical-Conditions-and-Treatments/Herniated-Disc
