What is a Rotator Cuff Injury?
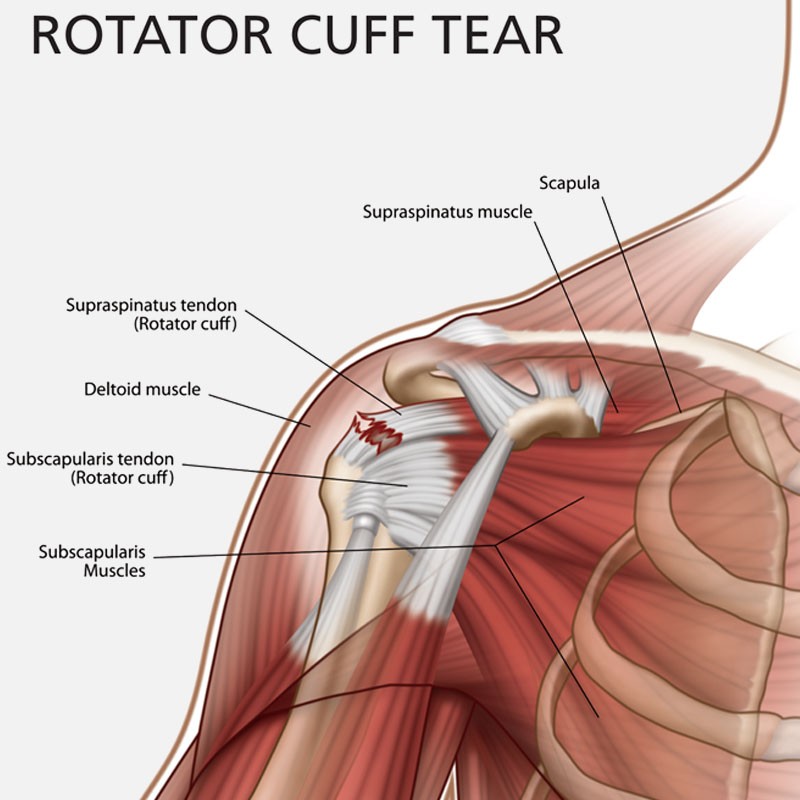
The rotator cuff is a group of muscles and tendons which encircle the shoulder joint, keeping the head of your upper arm bone steadily within the shallow socket of the shoulder. A rotator cuff injury could cause a dull pain in the shoulder, which usually worsens with use of the arm away from the body.
Rotator cuff injuries are common and increase with the age. These might happen earlier in people who have jobs which need repeatedly performing overhead motions. Instances include painters and carpenters.
Many people with rotator cuff disease could manage their symptoms and return to activities with physical therapy exercises which improve flexibility and strength of the muscles surrounding the shoulder joint.
Sometimes, rotator cuff tears might happen as a result of a single injury. In those situations, medical assessment must be provided as soon as possible to discuss the role of surgery. Extensive rotator cuff tears might not be fixable, and transfer of alternative tendons or joint replacement might be possible.
Rotator Cuff Injury Symptoms
The pain related with a rotator cuff injury might:
- Be described as a dull pain deep in the shoulder
- Disturb sleep
- Make it hard to comb your hair or reach behind your back
- Be followed by arm weakness
When should you see a doctor?
Shoulder pain which is short-lived might be assessed by your family primary care physician. See your primary care physician right away if you have immediate weakness in your arm after an injury.
Causes
Rotator cuff disease might be the consequence of either a substantial injury to the shoulder or to progressive degeneration or wear and tear of the tendon tissue. Repeated overhead activity or heavy lifting over a prolonged period of time might irritate or affect the tendon.
Risk Factors
The following factors might increase your risk of having a rotator cuff injury:
- Age – When you get older, your risk of a rotator cuff injury rises. Rotator cuff tears or injuries are most common in people older than 60.
- Construction jobs – Occupations like carpentry or house painting need repeated arm motions, usually overhead, which could damage the rotator cuff over time.
- Family history – There might be a genetic component involved with rotator cuff injuries as they appear to happen more commonly in certain families.
shoulder rotator cuff injury
Complications
Without the treatment, rotator cuff complications might lead to permanent loss of motion or weakness, and might result in progressive degeneration of the shoulder joint. However, resting your shoulder is required for your recovery, keeping your shoulder immobilized for a prolonged time could cause the connective tissue enclosing the joint to become thickened and tight or frozen shoulder.
Prevention
If you are at risk of rotator cuff injuries or if you have had a rotator cuff injury in the past, daily shoulder strengthening exercises could help stop future injury.
Most of the people exercise the front muscles of the chest, shoulder and upper arm, but it is equally crucial to strengthen the muscles in the back of the shoulder and around the shoulder blade to improve shoulder muscle balance. Your primary care physician or a physical therapist could help you plan an exercise routine.
Diagnosis
During the physical examination, your primary care physician will press on different parts of your shoulder and move your arm into different positions. He or she will also examine the strength of the muscles around your shoulder and in your arms.
In some of the cases, he or she might suggest imaging tests, like:
- X-rays – However, a rotator cuff tear would not show up on an X-ray, this test could visualize bone spurs or other potential causes for your pain — like arthritis.
- Ultrasound – This type of test uses sound waves to produce pictures of structures within your body, especially soft tissues like muscles and tendons. It permits dynamic testing, evaluating the structures of your shoulder as they move. It also permits a quick comparison between the damaged shoulder and the healthy shoulder.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) – This technology uses radio waves and a strong magnet. The pictures obtained display all structures of the shoulder in great detail. The quality of the pictures depends greatly upon the quality of the equipment used.
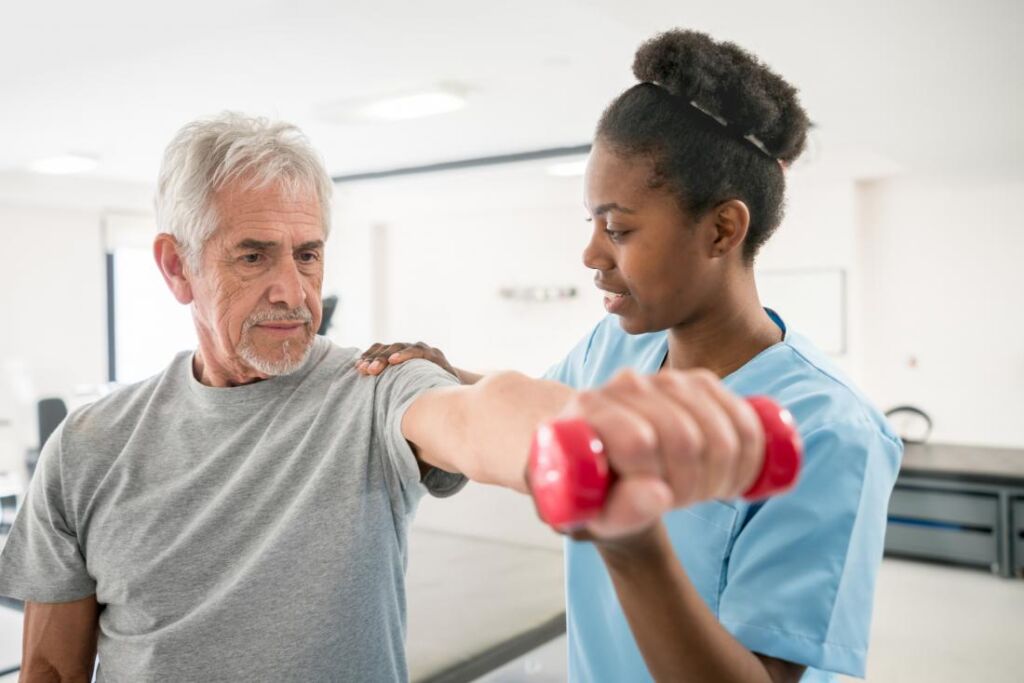

Rotator Cuff Injury Treatment
Conservative treatments like rest, ice and physical therapy sometimes are all that is required to recover from a rotator cuff injury. If your injury is serious, you might require surgery.
Injections
If conservative treatments have not lowered your pain, your primary care physician might suggest a steroid injection into your shoulder joint, particularly if the pain is interfering with your sleep, daily activities or physical therapy. While such shots are usually momentarily helpful, they must be used judiciously, as they could contribute to weakening of the tendon and might lower the success of surgery if this is eventually required.
Therapy
Physical therapy is generally one of the first treatments your primary care physician might recommend. Exercises customized to the certain location of your rotator cuff injury could help restore flexibility and strength to your shoulder. Physical therapy is also a crucial part of the recovery process after rotator cuff surgery.
Many different forms of surgeries are available for rotator cuff injuries, including:
- Arthroscopic tendon repair – In this technique, surgeons insert a tiny camera also known as arthroscope and tools through small incisions to reattach the torn tendon to the bone.
- Open tendon repair – In some of the situations, an open tendon repair might be a better alternative. In these forms of surgeries, your surgeon works through a larger incision to reattach the affected tendon to the bone.
- Tendon transfer – If the torn tendon is too affected to be reattached to the arm bone, surgeons might decide to use a nearby tendon as a replacement.
- Shoulder replacement – Massive rotator cuff injuries might need shoulder replacement surgery. To improve the artificial joint’s stability, an innovative technique (reverse shoulder arthroplasty) installs the ball part of the artificial joint onto the shoulder blade and the socket part onto the arm bone.
If you or anyone you know is suffering from rotator cuff injury, our expert providers at Zenith Injury Relief & Wellness Clinic will take care of your health and help you recover.
Call 972-210-0033 to schedule your appointment , and begin living your life pain free.
